Introduction
Branch and Bound is an important problem-solving and optimization technique used in Artificial Intelligence and Operations Research. It is mainly applied to problems where we want to find the best (optimal) solution among many possible solutions, such as minimum cost or maximum profit problems.
Unlike blind search methods, Branch and Bound uses intelligent pruning to reduce the search space. It avoids exploring paths that cannot lead to a better solution, thereby saving time and computational effort.
Definition
Branch and Bound is a systematic search algorithm that explores a solution space by branching into subproblems and uses bounds (limits on the best possible solution) to eliminate non-promising paths.
In simple words:
Branch and Bound explores only those paths that can lead to an optimal solution and ignores the rest.
Basic Idea of Branch and Bound
The algorithm works on two main principles:
- Branching
- Divide the main problem into smaller subproblems
- Each subproblem represents a partial solution
- Bounding
- Calculate a bound (best possible value) for each subproblem
- If a subproblem cannot give a better solution than the current best, it is discarded
This approach drastically reduces unnecessary exploration.
Important Terminology
- State Space Tree: Tree representing all possible solutions
- Node: A partial or complete solution
- Branching: Expanding a node into child nodes
- Bound: Estimated best possible value from a node
- Pruning: Eliminating nodes that cannot produce better solutions
- Optimal Solution: Best solution according to the problem objective
Working of Branch and Bound (Step by Step)
- Start with the root node representing the initial problem
- Calculate the bound value for the root
- Branch the root into child nodes
- For each child:
- Compute its bound
- Compare bound with current best solution
- Discard (prune) nodes whose bound is worse than the current best
- Select the most promising node for further expansion
- Repeat until:
- All promising nodes are explored
- The best solution found is the optimal solution
Diagrammatic Explanation
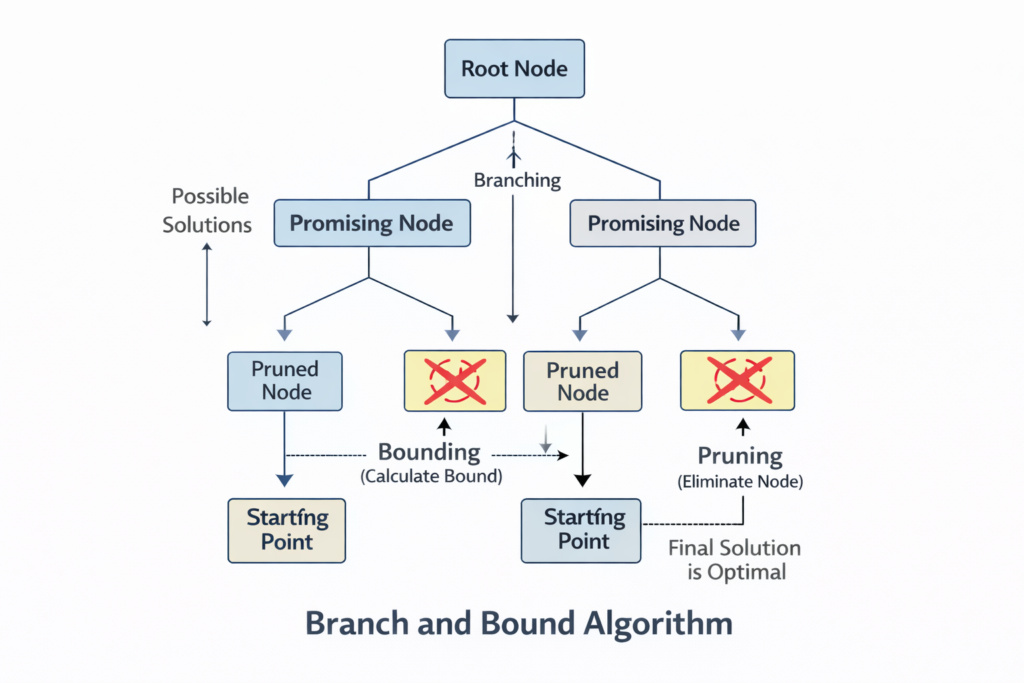
Explanation of Diagram
- Root represents the complete problem
- Branches show subproblems
- Some branches are cut off (pruned)
- Only promising paths are explored
- Final solution is optimal
Types of Branch and Bound
1. FIFO Branch and Bound
- Nodes expanded in first-in-first-out order
- Uses a queue
- Simple but may explore unnecessary nodes
2. LIFO Branch and Bound
- Uses stack-based approach
- Depth-first style
- Requires less memory
3. Least Cost (Best-First) Branch and Bound
- Expands node with best bound value first
- Uses priority queue
- Most efficient and commonly used
Example (Conceptual)
Consider a Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP):
- Each node represents a partial tour
- Bound = estimated minimum cost to complete the tour
- Paths with higher cost than current best are pruned
- Final tour found has minimum total distance
Applications of Branch and Bound
- Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP)
- 0/1 Knapsack Problem
- Job Scheduling
- Integer Programming
- Resource Allocation
- Network Design
- AI optimization problems
Advantages of Branch and Bound
- Guarantees optimal solution
- Reduces search space using pruning
- More efficient than brute force
- Systematic and organized approach
Disadvantages of Branch and Bound
- Worst-case time complexity is high
- Performance depends on bounding function
- May consume large memory
- Complex to implement for large problems
Time and Space Complexity
- Time Complexity: Exponential in worst case
- Space Complexity: Depends on number of active nodes stored
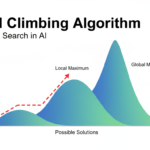
Branch and Bound vs Hill Climbing (Quick Insight)
- Branch and Bound is complete and optimal
- Hill Climbing is local and approximate
- Branch and Bound explores globally with pruning
- Hill Climbing uses local improvement only
Branch and Bound in Artificial Intelligence
In AI, Branch and Bound is used when:
- Exact optimal solution is required
- Search space is large but structured
- Heuristics can estimate good bounds
It is widely used in optimization-based AI problems.
Conclusion
Branch and Bound is a powerful optimization technique that systematically explores a problem space by dividing it into smaller subproblems and eliminating non-promising paths using bounds. Although it may have high worst-case complexity, its ability to guarantee optimal solutions makes it an essential algorithm in artificial intelligence and combinatorial optimization.